Drug Dosage Based on Units
Potencies of certain medications are based on their activity and are expressed in terms of units. Common drugs for which units are used include penicillin, insulin, bacitracin, heparin, nystatin, polymyxin, and vitamins A, D, and E. Units of activity are determined against specific biologic standards and vary between products. Thus, there is no cross relationship between the units of potency of one drug and the units of potency of another drug. Table A below illustrates that metric equivalency to units varies, with each drug using a “unit” system of measurement having its own conversion factor.
Table A: Examples of Drug Potency Equivalents
| Penicillin V Potassium, 1380-1610 units | 1 mg |
|---|---|
| Insulin Human, 27.5 units | 1 mg |
| Insulin Lispro, 27 units | 1 mg |
| Bacitracin Zinc, 65 units | 1 mg |
| Bacitracin Zinc, 65 units | 1 mg |
| Polymyxin B Sulfate, 6000 units | 1 mg |
| Vitamin D, 40000 units | 1 mg |
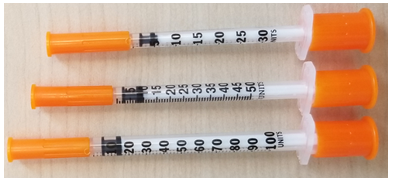
In addition to potencies of drugs being expressed in units, doses of these medications are also expressed in units. For example, commercially available preparations of insulin are standardized to contain either 100 or 500 units per milliliter of solution or suspension. These package strengths are designated as U-100 and U-500. Syringes are available that measure insulin dosage directly in units as shown in Figure- A below.
Figure A: Insulin Syringes 30 U, 50 U and 100 U
Calculation of dose or potency can be performed using ratio and proportion or dimensional analysis as shown below:
|
Solved Problem: You receive the following prescription at your pharmacy. How many days supply will the prescribed vial hold?
Approach: : This problem can be solved either by ratio and proportion or dimensional analysis. Set up a dimensional analysis so that your final answer is in days. The patient takes 25 units per day. $$ {day \over 25 \ units} \times {100 \ units \over ml} \times 10 \ ml = 40 \ days $$ Answer: 40 days Another drug whose dose and potency is expressed in Units is an anticoagulant drug called Heparin. It is a large sulfated polysaccharide polymer obtained from animal sources. Heparin is given intravenously or subcutaneously for treatment of deep venous thrombosis (DVT), pulmonary embolism, and acute myocardial infarction. Heparin is available in various strengths ranging from 1 unit/ml to 20,000 units/ml. |
|
Solved Problem: Calculate the dose of heparin that was administered to a patient if the nurse injected 0.25 ml of heparin solution from a vial with a label stating 5000 units of heparin per ml. Approach: : Set up a ratio and proportion The patient takes 25 units per day. $$ {5000 \ units \ of \ heparin \over 1 \ ml} = {x \ units \ of \ heparin \over 0.25 \ ml} $$ Answer: : 1250 units |